선형데이터구조, 스택(Stack) #2 Stack Collection Framework (JAVA)
2021. 9. 16. 12:15ㆍDataStructure
개요
자바의 컬렉션 프레임워크(Collection Framework)는 데이터 구조인 스택을 구현한 Stack 클래스를 제공합니다. 이 Stack 클래스는 LIFO(Last-In-First-Out) 원칙에 기반하여 수행됩니다. 기본적인 push, pop 연산뿐만 아니라 empty, search, peek 연산도 제공합니다. Stack 클래스는 Vector 클래스로부터 상속되었습니다. 아래의 그림은 Stack 클래스의 상속관계를 알려줍니다.
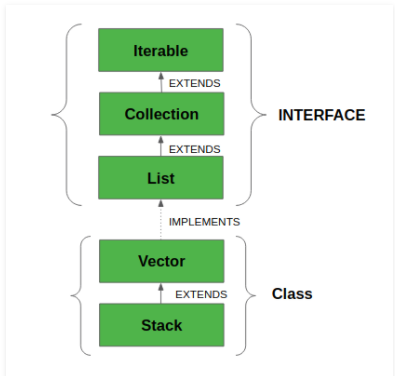
위의 그림을 보면 Stack 클래스는 Vector 클래스로부터 상속(Extend)받은 것을 알 수 있으면 부모 클래스인 Vector 클래스는 List 인터페이스로부터 구현됨을 알 수 있습니다.
Declaration
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>Stack 클래스 객체 생성
Stack<E> stack = new Stack<E>();E는 Object의 타입입니다. Stack 클래스는 java.util.stack 패키지를 사용합니다. 위와 같이 수행하면 빈 Stack 객체가 생성합니다.
// 스택 컬렉션 프레임워크를 위한 예제
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Test
{
// 스택에 정수 0~4를 추가합니다.
static void stack_push(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
}
// 스택으로부터 데이터를 제거합니다.
static void stack_pop(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
System.out.println("Pop Operation:");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Integer y = (Integer) stack.pop();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
// 스택의 제일 꼭대기에 존재하는 데이터를 확인합니다.
static void stack_peek(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
Integer element = (Integer) stack.peek();
System.out.println("Element on stack top: " + element);
}
// 스택의 요소를 탐색합니다.
static void stack_search(Stack<Integer> stack, int element)
{
Integer pos = (Integer) stack.search(element);
if(pos == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at position: " + pos);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}Output
Pop Operation:
4
3
2
1
0
Element on stack top: 4
Element is found at position: 3
Element not foundStack 클래스의 다양한 연산 수행
1. 요소 추가 : 스택에 요소를 추가하기 위해 push 메소드를 사용합니다. push 메소드를 사용하면 스택에 꼭대기에 요소를 추가합니다.
// 스택에 요소를 추가하는 예제
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 스택 초기화
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
// 제너릭(Generics)을 활용한 스택의 초기화
Stack<String> stack2 = new Stack<String>();
// 요소 추가
stack1.push(4);
stack1.push("All");
stack1.push("Geeks");
stack2.push("Geeks");
stack2.push("For");
stack2.push("Geeks");
System.out.println(stack1); // Expected Output : [4, All, Geeks]
System.out.println(stack2); // Expected Output : [Geeks, For, Geeks]
}
}Output
[4, All, Geeks]
[Geeks, For, Geeks]
2. 요소에 접근
Stack의 꼭대기 데이터를 참조하기 위해서 peek 메소드를 사용합니다. peek 메소드를 수행하면 꼭대기의 데이터를 참조만 할뿐 삭제하지는 않는다.
// 스택의 peek 메소드 실습 예제
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
// 데이터 추가
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("Geeks");
stack.push("For");
stack.push("Geeks");
// 초기 스택 출력
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack); // Expected Output : [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
// 스택의 꼭대기 데이터 참조
System.out.println("The element at the top of the"
+ " stack is: " + stack.peek()); // Expected Output : Geeks
// peek 메소드 이후의 스택 상태 출력 => 변화 없음
System.out.println("Final Stack: " + stack); // Expected Output : [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
}
}Output
Initial Stack: [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
The element at the top of the stack is: Geeks
Final Stack: [Welcome, To, Geeks, For, Geeks]
3. 스택의 요소 제거 : 스택에서 요소드를 제거하기 위해서는 pop 메소드를 사용합니다. pop 메소드를 사용하면 스택의 꼭대기에 존재하는 데이터를 제거하고 값을 반환합니다.
// 스택의 pop 메소드 예제
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(15);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(5);
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack); // Expected Output : 10 15 30 20 5
// Stack 클래스의 pop 메서드 수행
System.out.println("Popped element: "
+ stack.pop()); // Expected Output : 5
System.out.println("Popped element: "
+ stack.pop()); // Expected Output : 20
// pop 메서드 수행 이후 스택의 상태 출력
System.out.println("Stack after pop operation "
+ stack); // Expected Output : [10, 15, 30]
}
}Output
Initial Stack: [10, 15, 30, 20, 5]
Popped element: 5
Popped element: 20
Stack after pop operation [10, 15, 30]
References
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-class-in-java/
'DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 선형데이터구조, 큐(Queue) #2 Queue Collection Framework (JAVA) (0) | 2021.09.16 |
|---|---|
| 선형데이터구조, 큐(Queue) #1 큐 소개 및 배열기반 구현 (0) | 2021.09.16 |
| 선형데이터구조, 스택(Stack) #1 스택 구조 소개 및 구현 (0) | 2021.09.15 |
| 선형데이터구조, 연결리스트(LinkedList) #3 addFirst/addLast 메서드 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| 선형데이터구조, 연결리스트(LinkedList) #2 노드와 크기 및 경계조건 (0) | 2021.09.14 |