2021. 9. 10. 14:20ㆍDataStructure
1. ArrayList Collection Framework 소개
ArrayList는 java.util 패키지에서 컬렉션 프레임워크(Collection Framework) 중 하나입니다. ArrayList는 자바에서 동적인 배열을 제공합니다. 그래서 ArrayList는 표준 배열보다 느리지만 배열의 조작(삽입,삭제,조회)이 많이 필요할 경우 유용합니다. ArrayList 클래스의 상속관계는 다음과 같습니다.
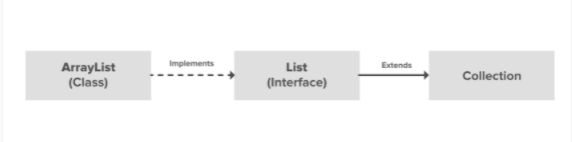
위의 그림에서 List 인터페이스에서 표준화된 리스트 연산(삽입, 삭제, 조회 등)을 선언하고 ArrayList 클래스에서 List 인터페이스 선언된 메소드들을 실제로 구현합니다. 하지만 java.util.ArrayList 클래스는 이미 구현이 완료되었기 때문에 저희 입장에서는 ArrayList 클래스 객체를 생성한 다음 사용만 하면 됩니다.
2. ArrayList 생성 및 기본적인 사용 테스트
// ArrayList 컬렉션 프레임워크의 생성 및 기본적인 사용 테스트
@Test
void createAndUsingArrayListTest() {
int n = 5;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(5);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println(list); // Expected Output : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
list.remove(3);
System.out.println(list); // Expected Output : [1, 2, 3, 5]
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++)
{
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " "); // Expected Output : 1 2 3 5
}
System.out.println();
}
3. ArrayList add() 메서드 사용 테스트
- add(Object obj) : ArrayList에서 끝쪽에 Object를 추가합니다.
- add(int index, Object obj) : ArrayList에서 index번째 위치에 obj 객체를 추가합니다. index번째 위치에 데이터가 존재한다면 오른쪽으로 한칸씩 이동합니다.
// ArrayList 컬렉션 프레임워크의 add() 메서드 테스트
@Test
void addArrayListTest() {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add(1,"real");
System.out.println(list); // Expected Output : [hello, real, world]
}4. ArrayList set() 메서드 사용 테스트
- set(int index, Object obj) : ArrayList에서 index번째 위치의 값을 obj 객체로 변경합니다.
// ArrayList 컬렉션 프레임워크의 set() 메서드 테스트
@Test
void setArrayListTest() {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add(1,"world");
System.out.println(list); // Expected Output : [hello, world, world]
list.set(1, "real");
System.out.println(list); // Expected Output : [hello, real, world]
}5. ArrayList remove() 메서드 사용 테스트
- remove(Object obj) : ArrayList에서 obj 객체를 찾아서 제거합니다. 만약 리스트에서 중복된 값이 존재한다면 제일 앞쪽의 값을 제거합니다. 값을 제거하면 뒤에 존재하는 데이터들은 왼쪽으로 이동합니다.
- remove(int index) : ArrayList에서 index번째 값을 제거합니다. 제거한 이후 뒤의 데이터들은 왼쪽으로 이동합니다.
// ArrayList 컬렉션 프레임워크의 remove() 메서드 테스트
@Test
void removeArrayListTest() {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add(1,"world");
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList : " + list); // Expected Output : [hello, world, world]
list.remove(1);
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + list); // Expected Output : [hello, world]
list.remove("world");
System.out.println("After the Object Removal " + list); // Expected Output : [hello]
}6. ArrayList 반복문 사용 테스트
// ArrayList 컬렉션 프레임워크의 loop 테스트
@Test
void loopArrayListTest()
{
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
// get 메서드를 활용한 요소 참조
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) // Expected Output : 1 2 3
{
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 각각의 요소를 가져와서 출력
for(int item : list) // Expected Output : 1 2 3
{
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
7. 중요 기능들
- ArrayList는 AbstractList 클래스와 List 인터페이스를 상속합니다.
- ArrayList는 객체 생성시 사이즈를 설정하고 생성이 가능합니다. 그러나 사이즈는 ArrayList의 데이터 수들이 증가하거나 줄어들 경우 자동적으로 증가/감소합니다.
- 자바 ArrayList는 우리에게 리스트에 랜덤 엑세스(Random Access)를 허용합니다.
- ArrayList의 저장 타입으로 Primitive Types(int, double, char 등)들은 허용하지 않습니다. 그래서 Primitive Types 들을 저장하기 위해서 래퍼 클래스(Wrapper Class)가 필요합니다. 래퍼 클래스로는 Integer, Double, Boolean 래퍼 클래스 등이 존재합니다.
- 자바에서 ArrayList 클래스는 C++의 vector로 보일수 있습니다.
- ArrayList 클래스는 비동기적입니다. 자바의 동기화된 클래스는 Vector 클래스가 있습니다.
8. ArrayList 상속 관계도
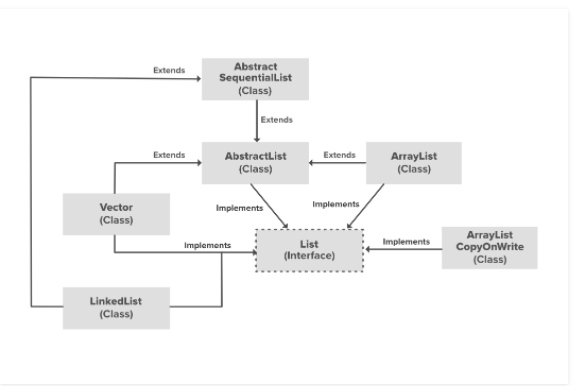
AbstractList, CopyOnWriteArrayList, AbstractSequentialList 클래스들은 List 인터페이스로부터 구현됩니다.
- AbstractList : 이 클래스는 AbstractList 클래스를 확장하고 get() 및 size() 메서드만 구현하면 되는 수정할 수 없는 목록을 구현하는데 사용됩니다.
- CopyOnWriteArrayList : 이 클래스는 List 인터페이스로부터 구현됩니다. CopyOnWriteArrayList 클래스는 목록의 새 복사본을 생성하여 모든 수정사항(add, set, remove 등)을 구현하는 ArrayList의 강화된 버전입니다.
- AbstractSequentialList : 이 클래스는 Collection 인터페이스와 AbstractCollection 클래스를 구현합니다. 이 클래스는 수정될 수 없는 리스트를 구현하는데 사용됩니다. 오직 get(), size() 메서드만 구현하고 AbstractList 클래스를 확장하는데 필요합니다.
9. ArrayList는 내부적으로 어떻게 동작하는가?
ArrayList는 동적인 배열이기 때문에 ArrayList의 요소를 추가하거나 제거할때 사이즈는 자동적으로 증가하거나 감소하기 때문에 이러한 과정중에 명시적으로 리스트의 사이즈를 설정하면 안됩니다. 그래서 실제 라이브러리 구현은 더 복합적입니다.
아래 설명은 만약 배열이 전부 차고 리스트에 요소를 추가할 때 배열의 작동을 설명하는 매우 기본적인 아이디어입니다.
- 힙 메모리(heap memory)에 더 큰 사이즈의 메모리 공간을 생성합니다.
- 현재 메모리 요소들을 새로운 메모리로 복사합니다.
- 새로운 요소는 더큰 메모리 공간쪽에 추가됩니다.
- 이전 메모리(old memory)는 삭제됩니다.
10. ArrayList 생성자
ArrayList를 생성하기 위해서는 객체 생성이 필요합니다. ArrayList는 다양한 생성자로 구성됩니다.
1. ArrayList() : 생성자에 공백으로 객체를 생성하는 경우입니다. ArrayList 객체는 비어있는 상태로 생성됩니다.
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(c);
2. ArrayList(Collection c) : Collection c의 요소들과 같이 초기화하는데 사용됩니다. 즉, ArrayList에 Collection c의 요소들이 같이 추가되어 생성됩니다.
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(c);
3. ArrayList(int capacity) : 객체 생성시 명시적으로 공간을 생성합니다.
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(N);
11. Java ArrayList Collection Framework Methods
| add(int index, Object element) | This method is used to insert a specific element at a specific position index in a list. |
| add(Object o) | This method is used to append a specific element to the end of a list. |
| addAll(Collection C) | This method is used to append all the elements from a specific collection to the end of the mentioned list, in such an order that the values are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| addAll(int index, Collection C) | Used to insert all of the elements starting at the specified position from a specific collection into the mentioned list. |
| clear() | This method is used to remove all the elements from any list. |
| clone() | This method is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| contains?(Object o) | Returns true if this list contains the specified element. |
| ensureCapacity?(int minCapacity) | Increases the capacity of this ArrayList instance, if necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. |
| forEach?(Consumer<? super E> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| get?(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this list. |
| indexOf(Object O) | The index the first occurrence of a specific element is either returned, or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| isEmpty?() | Returns true if this list contains no elements. |
| lastIndexOf(Object O) | The index of the last occurrence of a specific element is either returned or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| listIterator?() | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| listIterator?(int index) | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| remove?(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this list. |
| remove?(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it is present. |
| removeAll?(Collection c) | Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. |
| removeIf?(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| removeRange?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| retainAll?(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the specified collection. |
| set?(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. |
| size?() | Returns the number of elements in this list. |
| spliterator?() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
| subList?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| toArray() | This method is used to return an array containing all of the elements in the list in the correct order. |
| toArray(Object[] O) | It is also used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order same as the previous method. |
| trimToSize() | This method is used to trim the capacity of the instance of the ArrayList to the list’s current size. |
References
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/arraylist-in-java/
'DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 선형데이터구조, 연결리스트(LinkedList) #3 addFirst/addLast 메서드 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
|---|---|
| 선형데이터구조, 연결리스트(LinkedList) #2 노드와 크기 및 경계조건 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| 선형데이터구조, 연결리스트(LinkedList) #1 연결리스트 소개 (0) | 2021.09.14 |
| 선형데이터구조, 배열(Array) #2 배열을 이용한 리스트 구현 (JAVA) (0) | 2021.09.10 |
| 선형데이터구조, 배열(Array) #1 배열의 소개 (0) | 2021.09.09 |